NOTE: For prior parts in the Hizballah Cavalcade series you can view an archive of it all here.
–
Khamenei’s Cannon: .50 Caliber Anti-Material Rifles & Shia Fighters in Syria
By Phillip Smyth
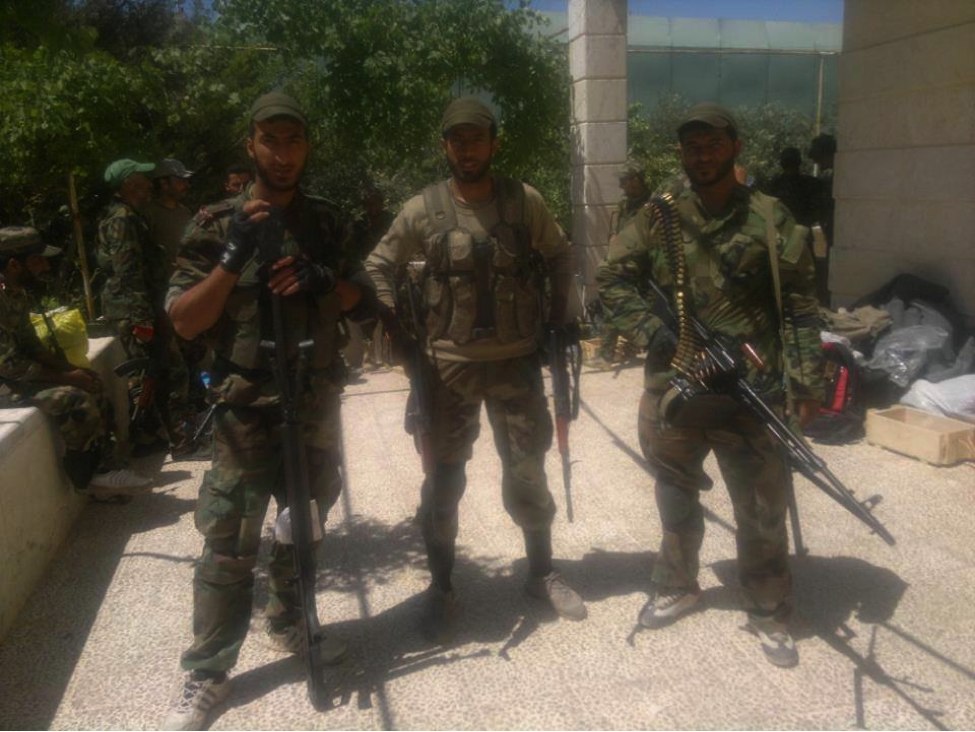

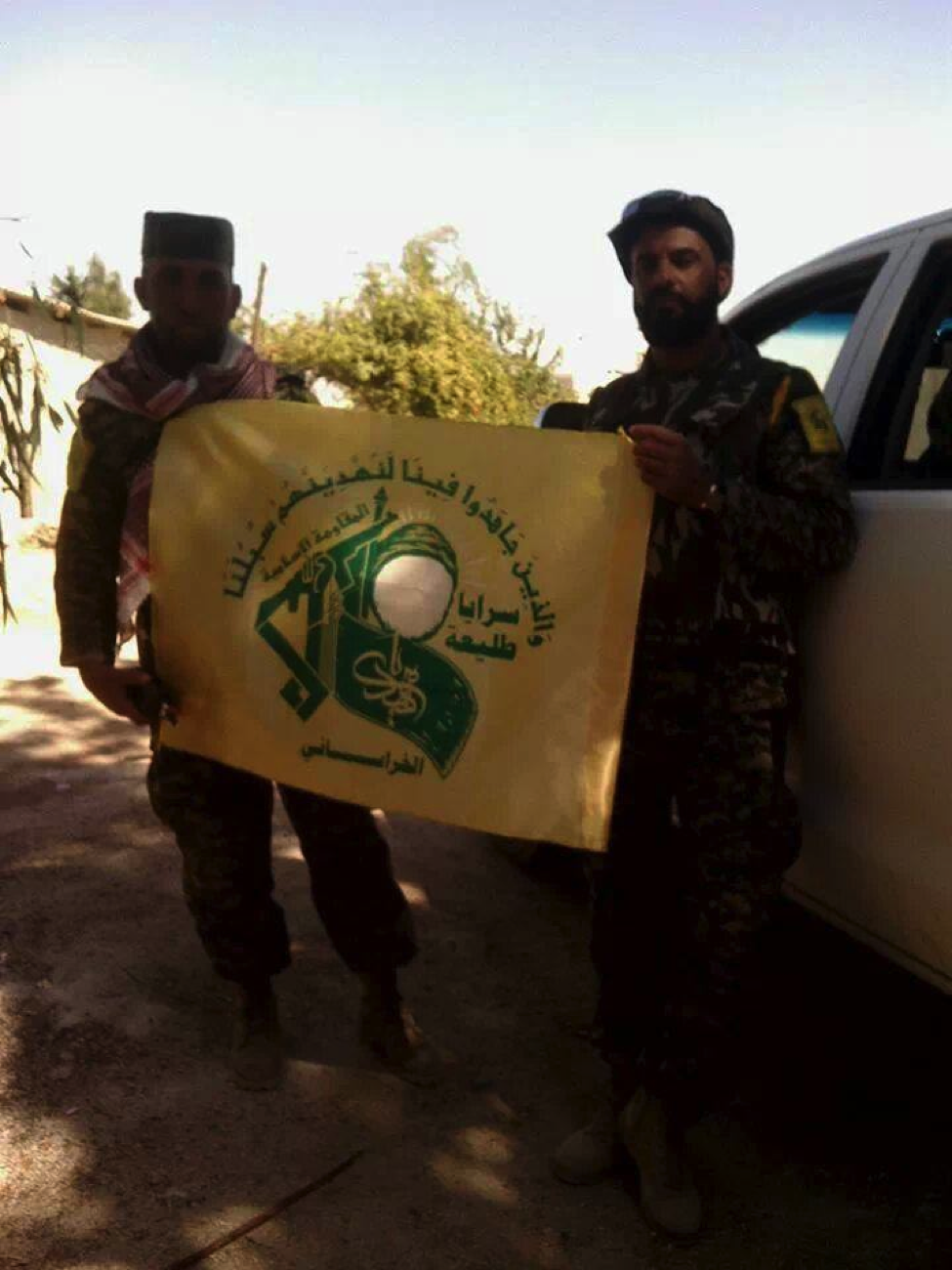
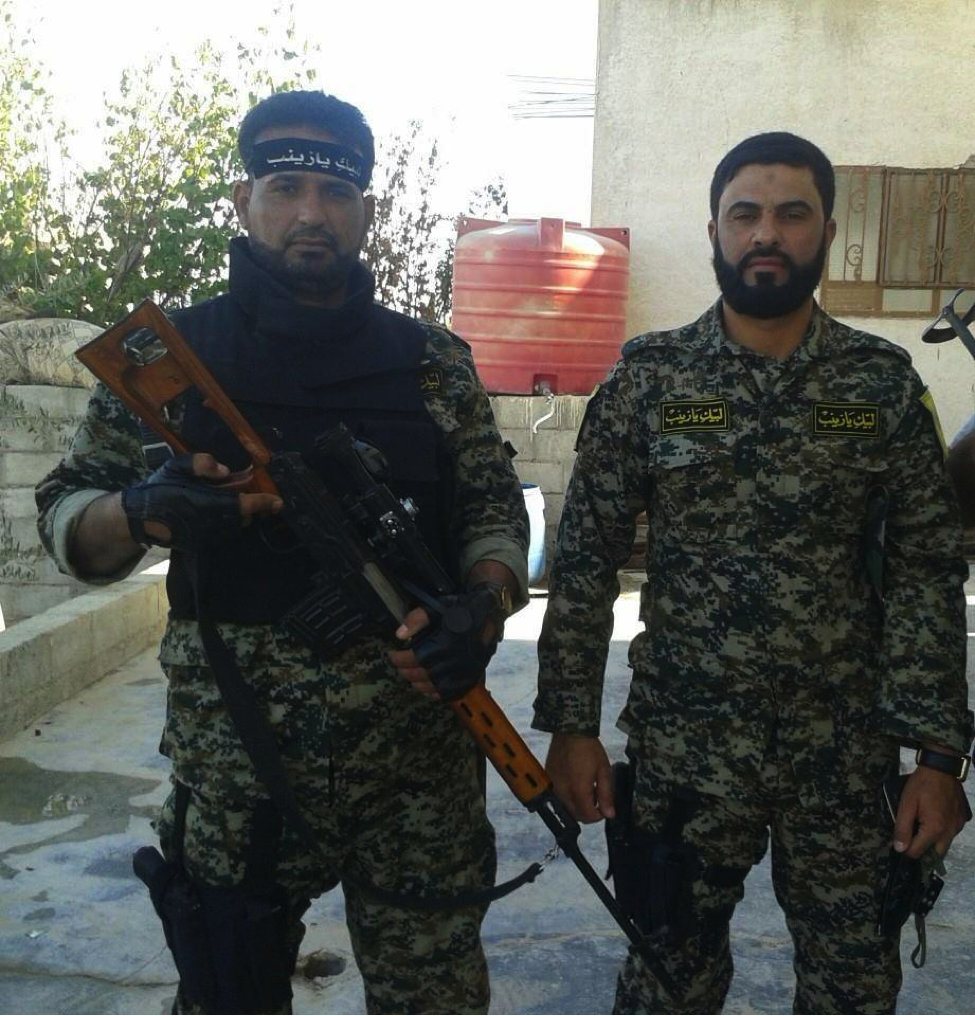
Figure 1: Combatants from Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir. The fighter on the left likely holds an Iranian-copy of the HS.50 rifle.
Since April 2013, around the same time Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas was first gaining broader exposure and name-recognition, another sub-trend started to appear in the photos showing Shia Islamist fighters in Syria. This trend remained minor and occasional. However, starting in October, there have been increasing examples of foreign Shia Islamist fighters being pictured with long range bolt-action anti-material rifles.[1]
It is possible these weapons were the bolt-action HS.50, .50 caliber (12.7x99mm) rifles produced by Austria’s Steyr Mannlicher. According to The Telegraph, 800 of the rifles were shipped to Iran in 2007.[2] However, according to the Brown Moses Blog, it is far more probable that these rifles are actually Iranian copies which were shipped to Syria.[3] Since the winter of 2012, pro-Iranian social media has also praised the Iranian-made copy of the rifle.[4] Still, serial numbers on the weapons are often hidden, making absolute confirmation difficult.
The original Steyr Mannlicher sale of these long-range weapons caused worries among British and U.S. policymakers and military personnel due to the fear they would be supplied to Iranian-created and supplied Shi’a Islamist “special groups” in Iraq. These groups included Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq and Kata’ib Hizballah. Both of these organizations are now sending forces to Syria.
Anti-material sniper rifles of this caliber have found a welcome place in Western military services. The U.S. military fields the M107 semi-automatic .50 caliber rifle as do a number of other militaries. In October, 2012 one of these weapons killed a Taliban member in Afghanistan from a distance of 2,475 meters.[5]
Presently in Syria, these types of rifles have been used by both rebels and pro-Assad forces. Nevertheless, the outfitting of highly organized foreign Shia fighter manned organizations may demonstrate a shift in tactics and training.
Groups using the rifle in Syria span the full spectrum of organizations backed by Iran. Lebanese Hizballah has been a primary poster of images with the weapon. Additionally, Iraq-based Harakat Hizballah al-Nujaba’s (a front for Kata’ib Hizballah and Asa’ib Ahl al-Haq) Syria-based front militias, Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir and Liwa’a al-Hamad have posted photos of their militants with the rifle. Iraq’s Badr Organization’s Quwet Shahid Muhammed Baqir Sadr and Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada have posted their own images of their fighters with the HS.50 type rifle. Other Shia fighters from unnamed organizations have also been pictured with the weapon.
Films featuring Shia militia groups using the HS. 50 type rifles in combat in Syria have been extremely rare. Usually only photos are posted.
The first film showing Shia Islamist militias in Syria using the rifle was posted to Facebook and YouTube pages associated with the Badr Organization’s Quwet Shahid Baqir Sadr (BOQSBS), the group’s expeditionary unit in Syria. The BOQSBS has also been a main poster of high-quality images showing their combatants wielding these types of anti-material rifles. Around a minute of footage showing BOQSBS fighters using the weapon was inserted into a much longer film made to demonstrate the group’s activities in Syria (see below at minute markers 1:59-2:23).
Due to the high level of operational security employed by these groups, potential failures or successes of the rifle in combat are often not showcased. Operations using the rifle have also not been detailed on the many social media pages run by Iranian-backed Shia militia groups inside Syria. In fact, the rifle has rarely been named or described by Shia Islamist militia pages. Nevertheless, these rifles have become a regular feature in images featuring fallen fighters.
Such a capability, even if deliberately showcased for propaganda purposes, should be taken seriously by regional and global military forces. Iranian equipped and trained snipers, utilizing smaller caliber rifles, demonstrated a lethal efficiency during the Iraq War (2003). Their utilization of smaller caliber-wielding snipers (particularly using the SVD-type rifles) demonstrates a concentration on sniping tactics.
Some Possible Reasons Why the Rifles Are Appearing More
- Propaganda Purposes: Some of the photos of fighters holding the rifle appear to be posed images meant to showcase the size of the weapon (representing power) in comparison to the fighter. Additionally, since it is probably a copy, showing the rifle in operations overseas is a sign that Iranian-made weapons are of a high quality. Proxy organizations may also see the rifle as a symbol of advancement and as a sign they are comparable to first-world armies. The weapon may also be a sign to rebel groups that Shia militants have more advanced capabilities.
- General Incorporation into the Order of Battle: The rifle could have possibly become more prolific with increased foreign-manned Shia militia operations.
- Offensive Operations: Since the start of main offensives in October and increase in numbers of Shia fighters, it is possible the rifle has found more use and acceptance by fighters.
The Rifle & Its Shia Islamist Users
Lebanese Hizballah:
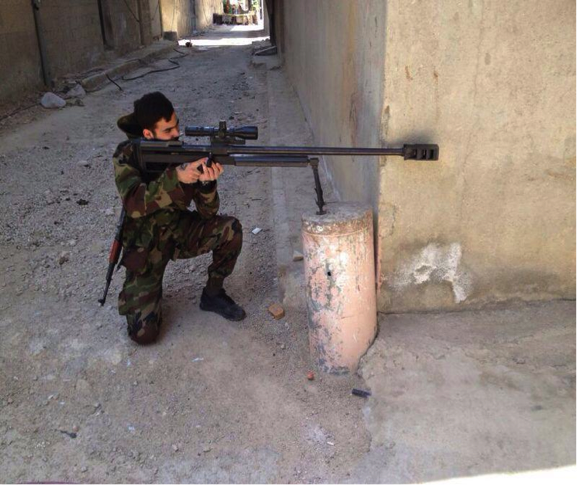


Figure 2: Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Hadi Nuwn shown holding the weapon on his shoulder. (Left)
Figure 3: Another posed-photo of Lebanese Hizballah’s Ali al-Hadi Nuwn. In this picture he is taking aim with the .50 caliber rifle. (Right)

Figure 4: Hizballah commander Ja’afar Husayn Hashim with the rifle. He was reported to have been killed in Syria on November 1, 2013.
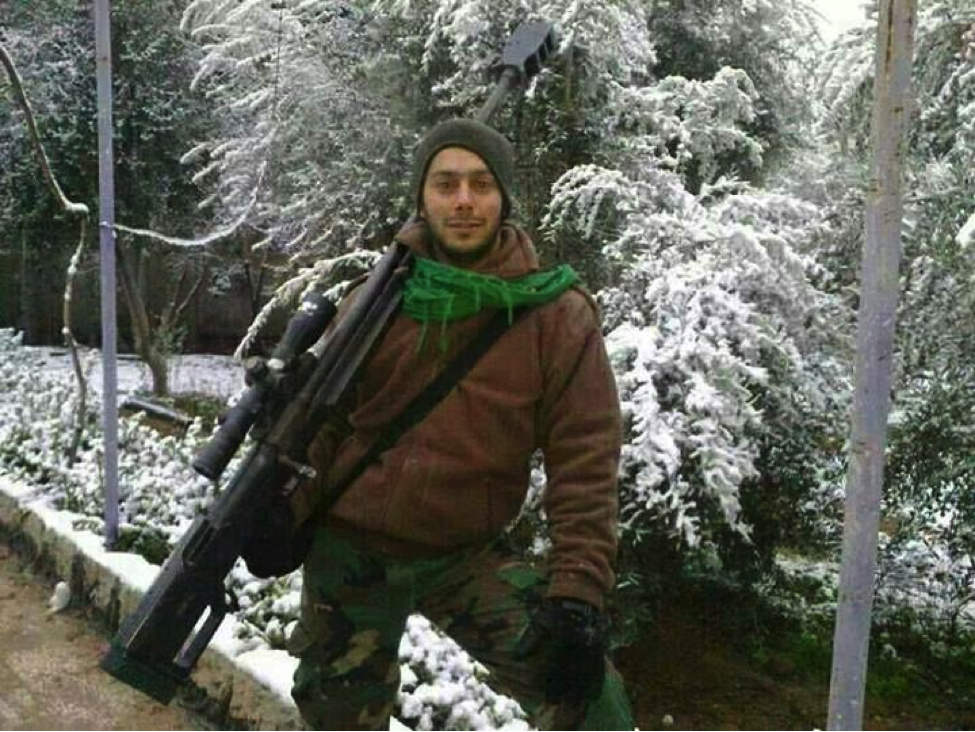

Figure 5: Hizballah’s Khadr Ahmed Matar, declared killed in Syria on December 2
0, is shown standing in the snow with the rifle.
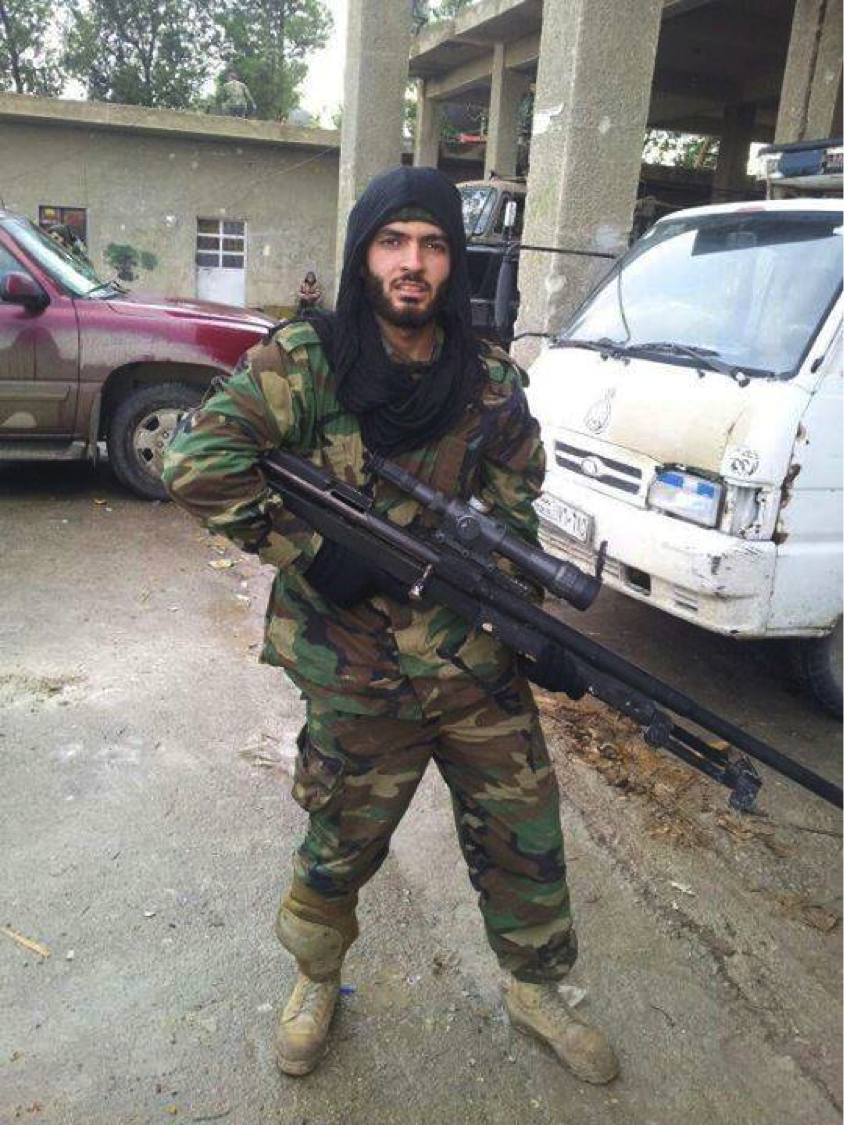

Figure 6: Qasim Ghamloush is shown holding the .50 caliber rifle. His death was announced by Hizballah on December 7, 2013.
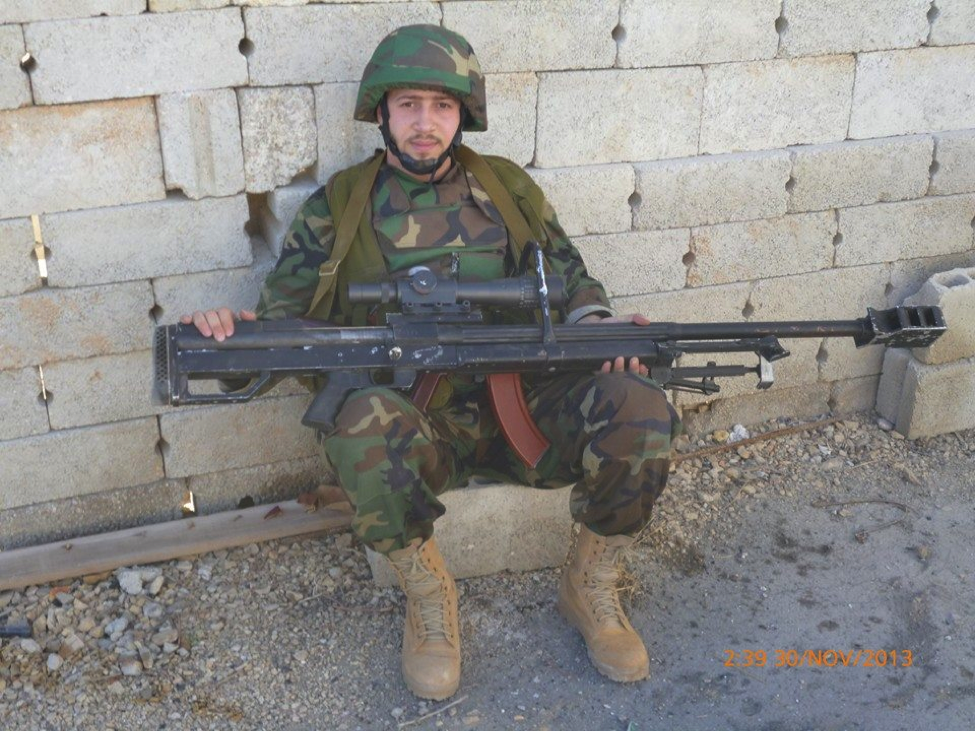

Figure 7: Ali Husayn Salah (A.K.A. Sheikh Hadi) is seen holding the rifle over his Kalashnikov-pattern weapon. Salah was also reported to have been killed in Syria on December 7, 2013.
Liwa’a al-Hamad:
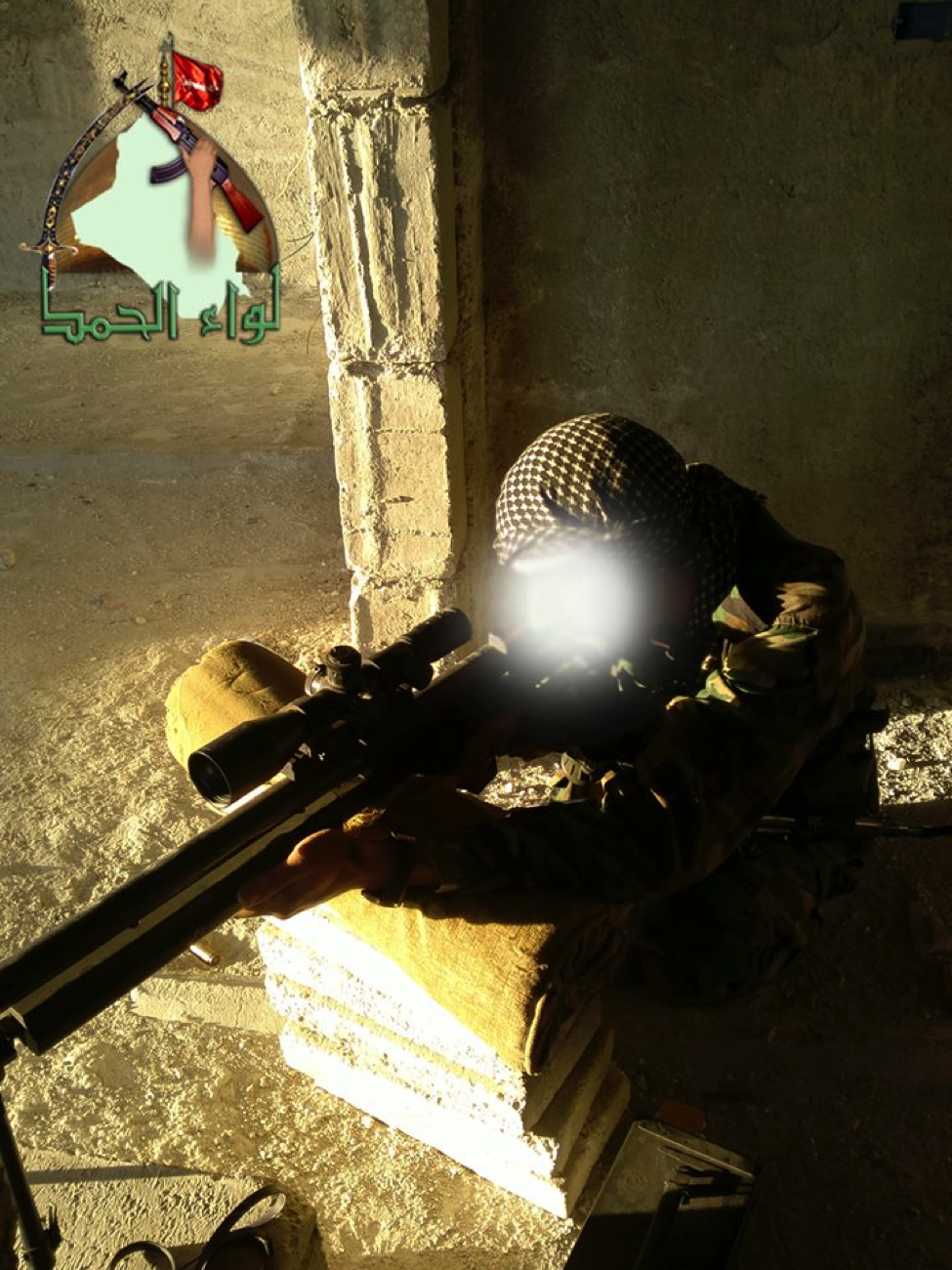

Figure 8: An October photo of a fighter from Liwa’a al-Hamad taking aim with the HS.50-type rifle.
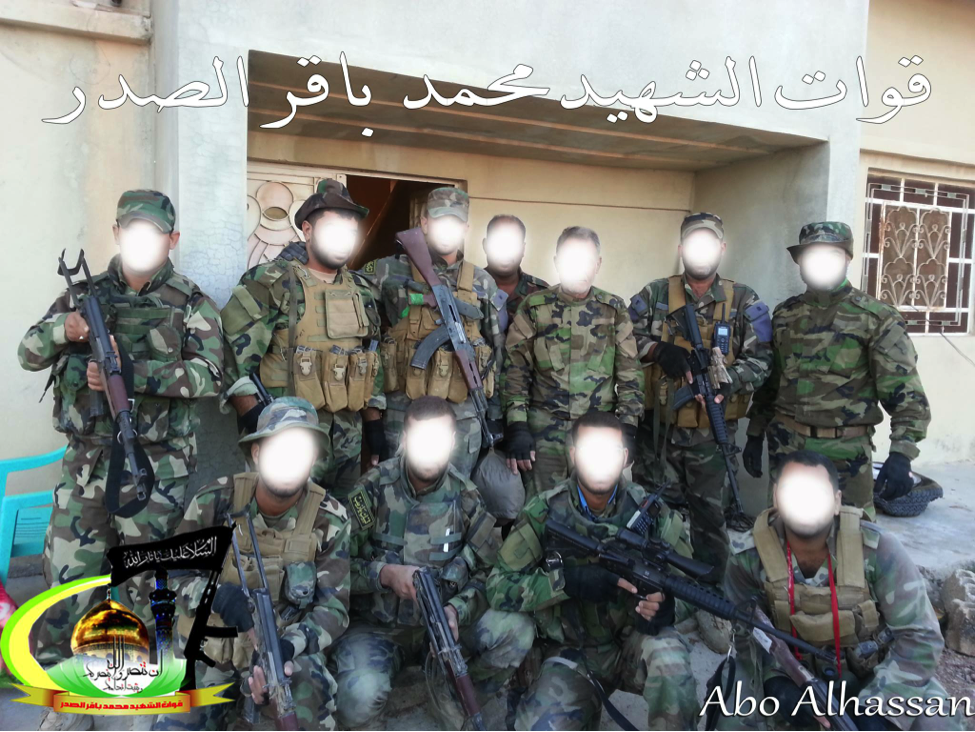
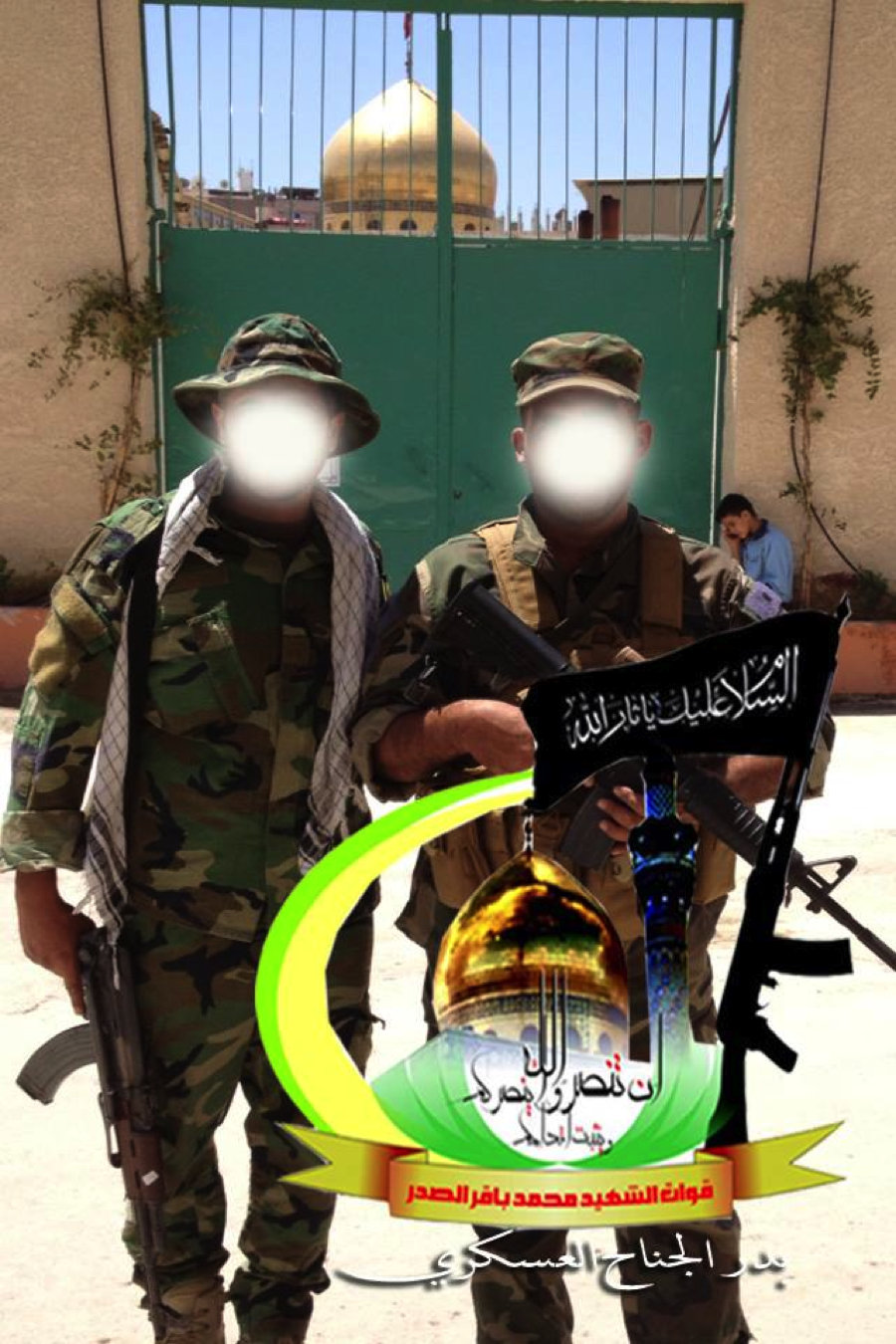
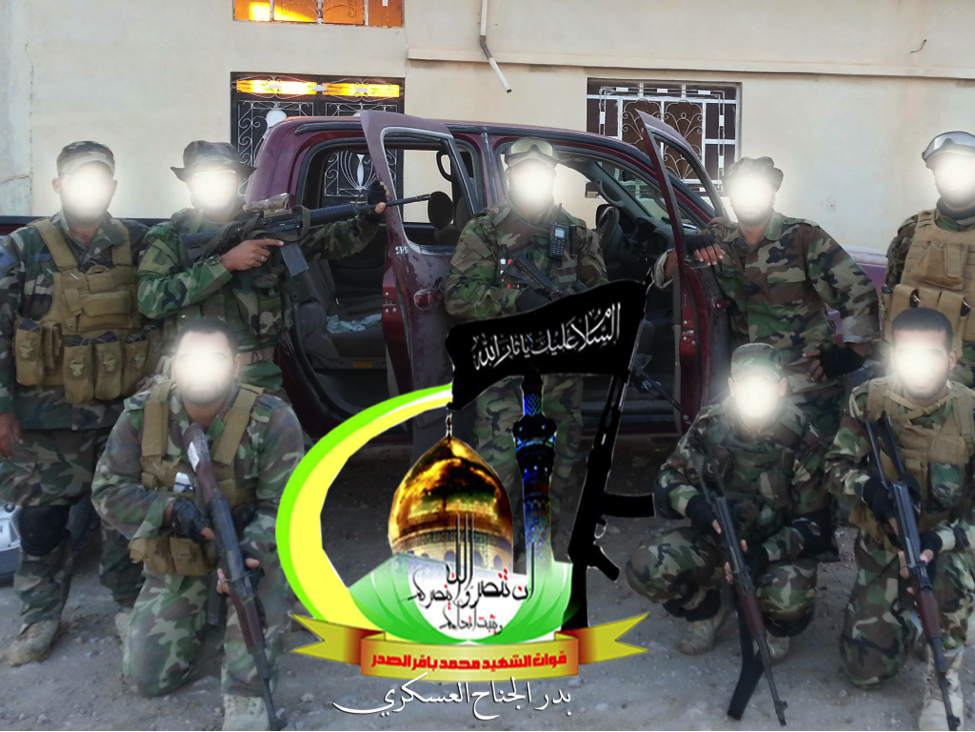
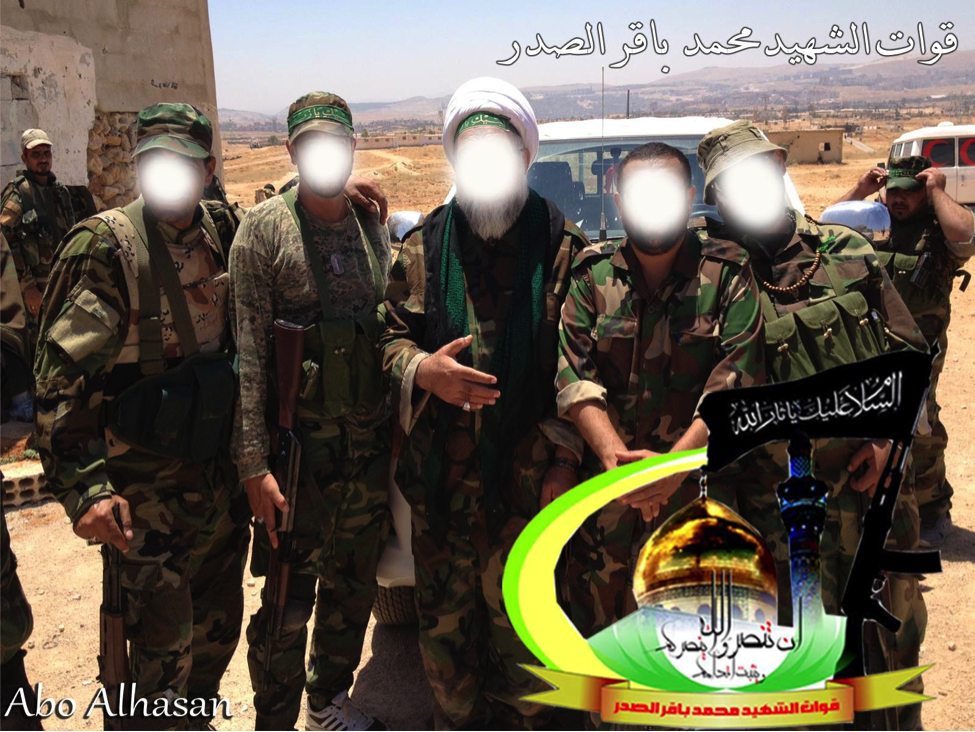
The Badr Organization – Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir Sadr

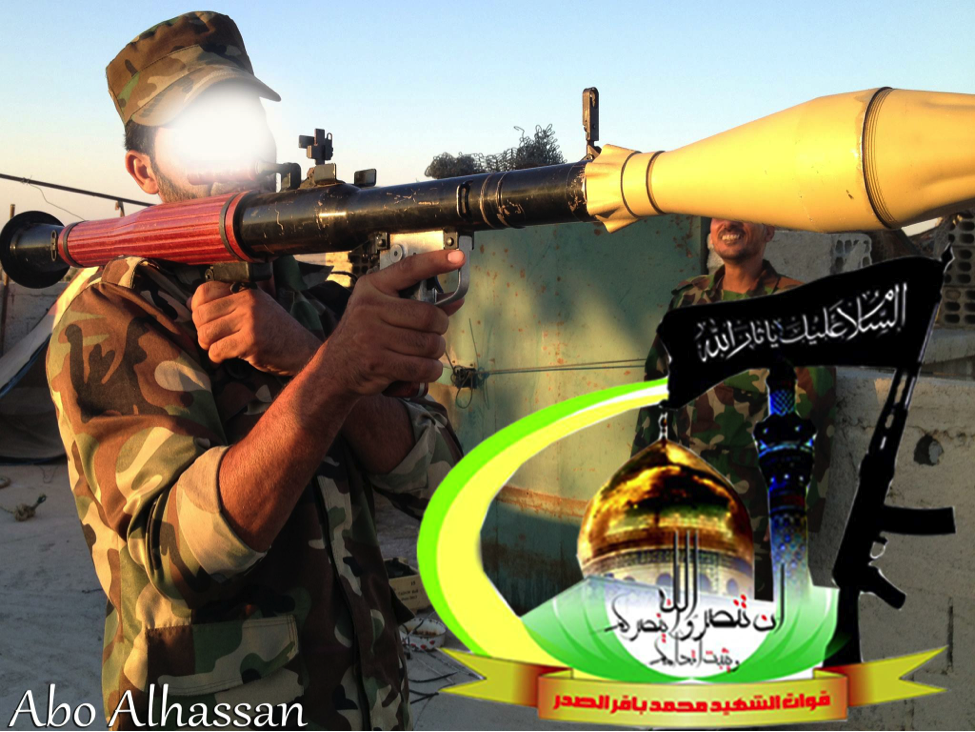
Figure 9: Following the announcement that the Badr Organization had created its own expeditionary force for Syria, this was one of the first photos they posted online.
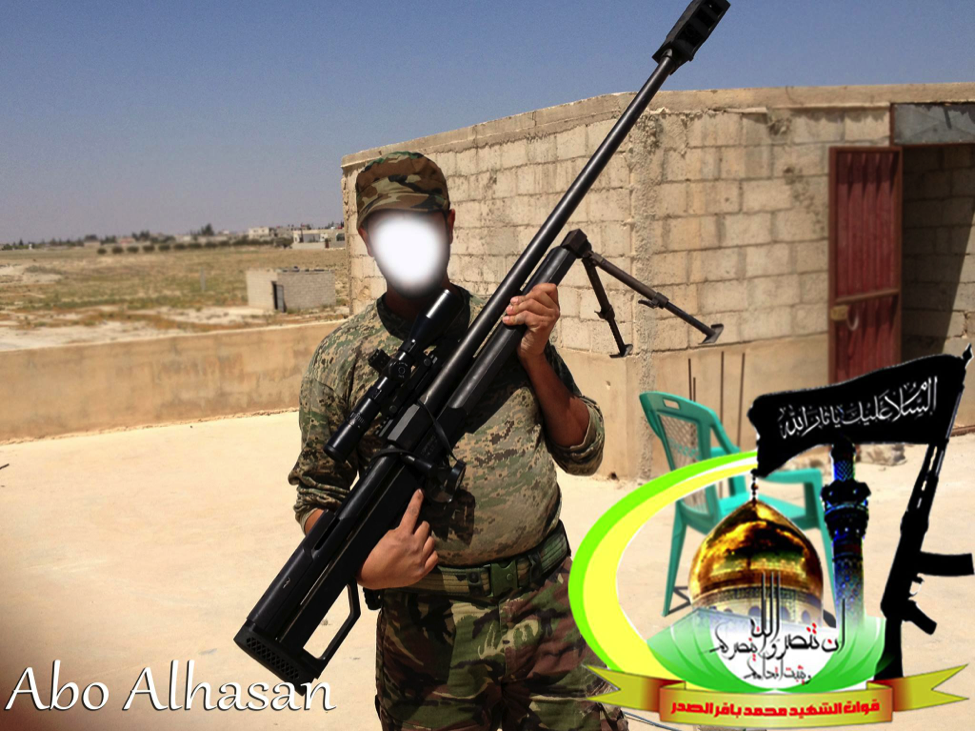

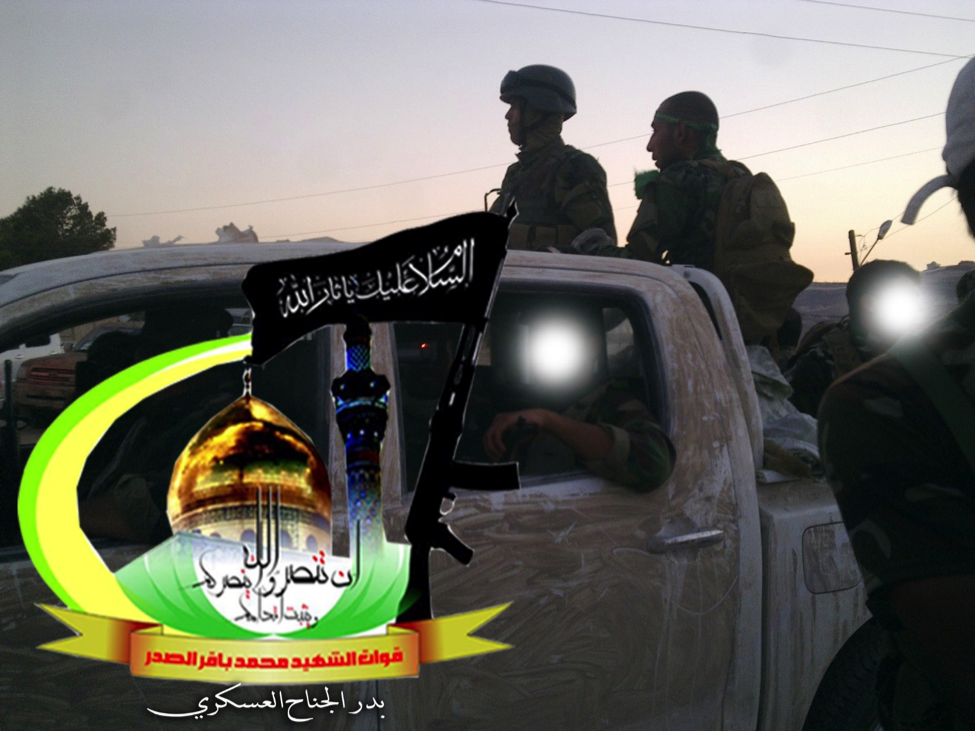
Figure 10: A Badr Organization-Quwet al-Shahid Muhammed Baqir al-Sadr is shown holding the HS. 50 type rifle.
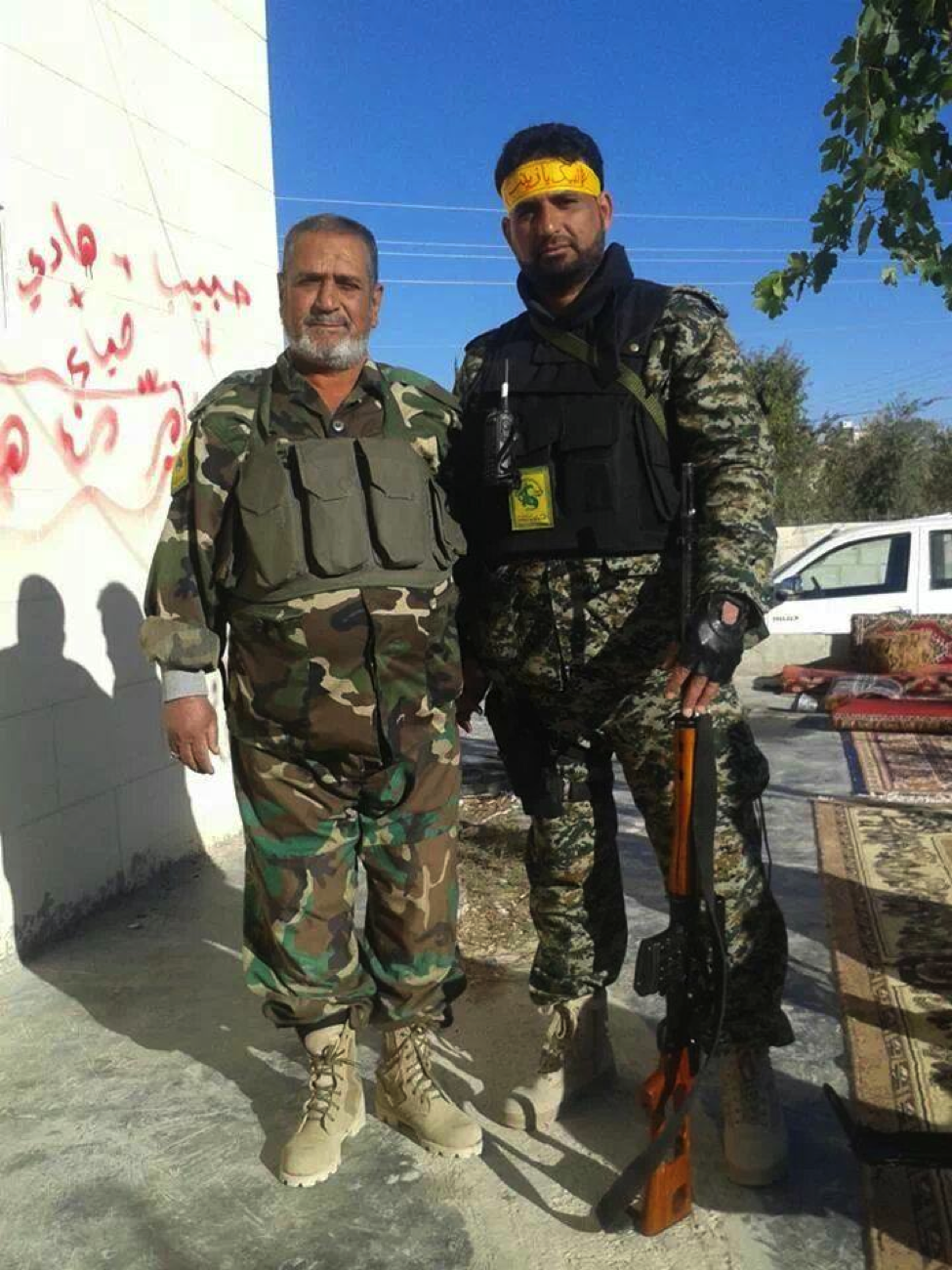
Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir:
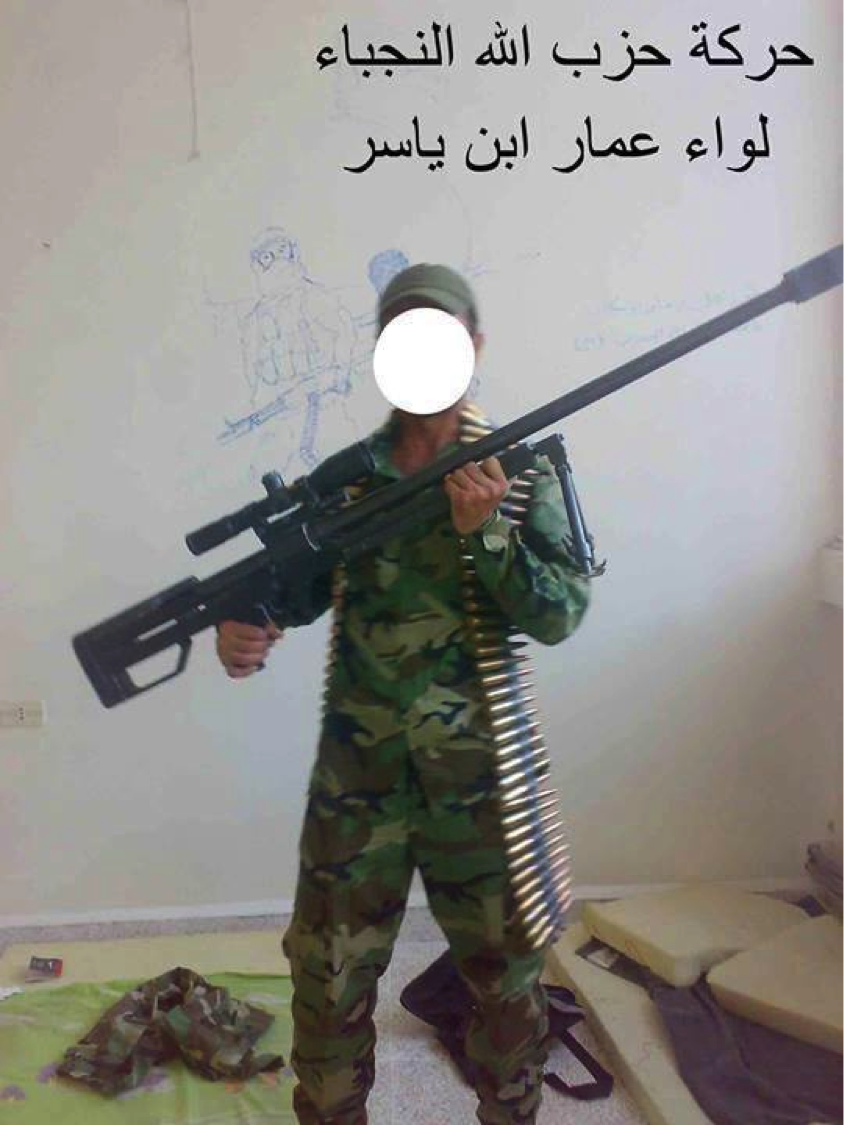
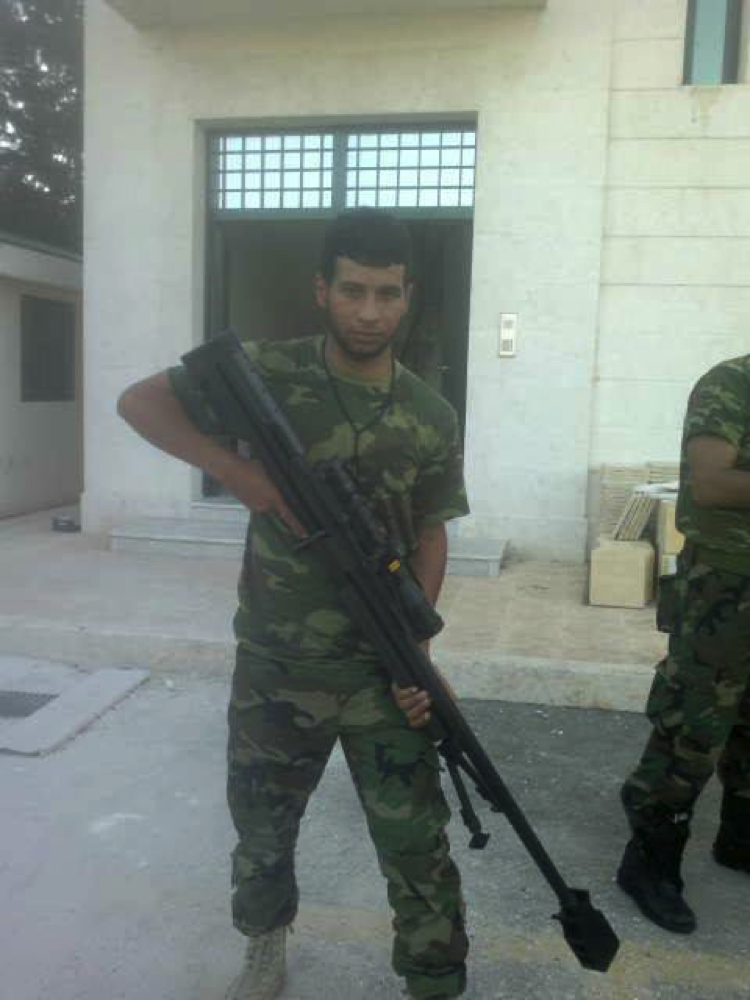


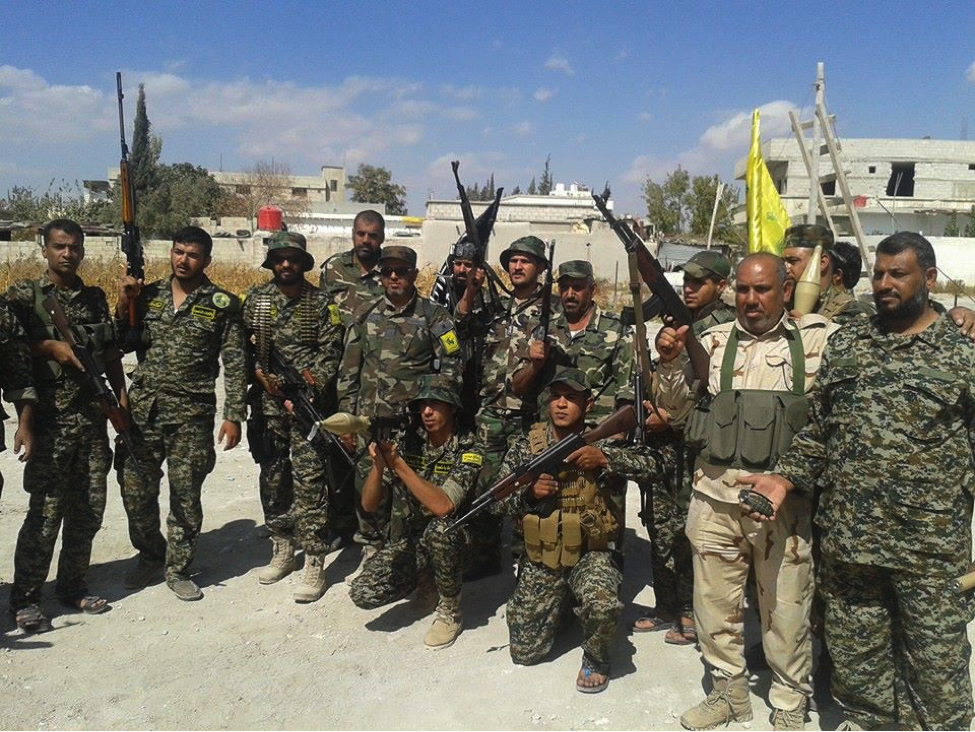
Figure 11: A commander from Liwa’a Ammar Ibn Yasir is seen holding the .50 caliber rifle.
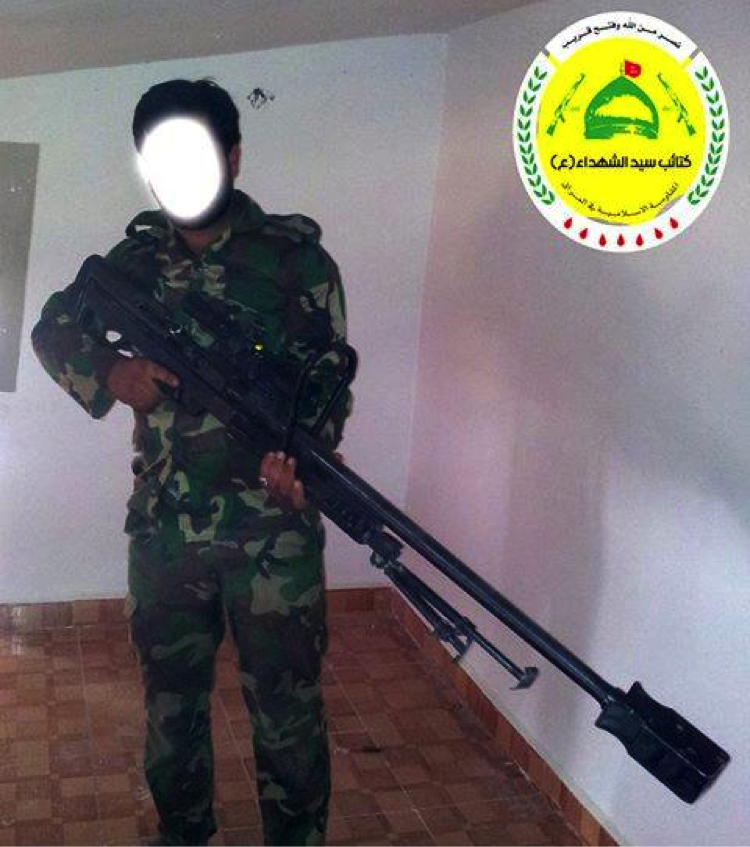
Kata’ib Sayyid al-Shuhada:

Fighters from Other Groups:
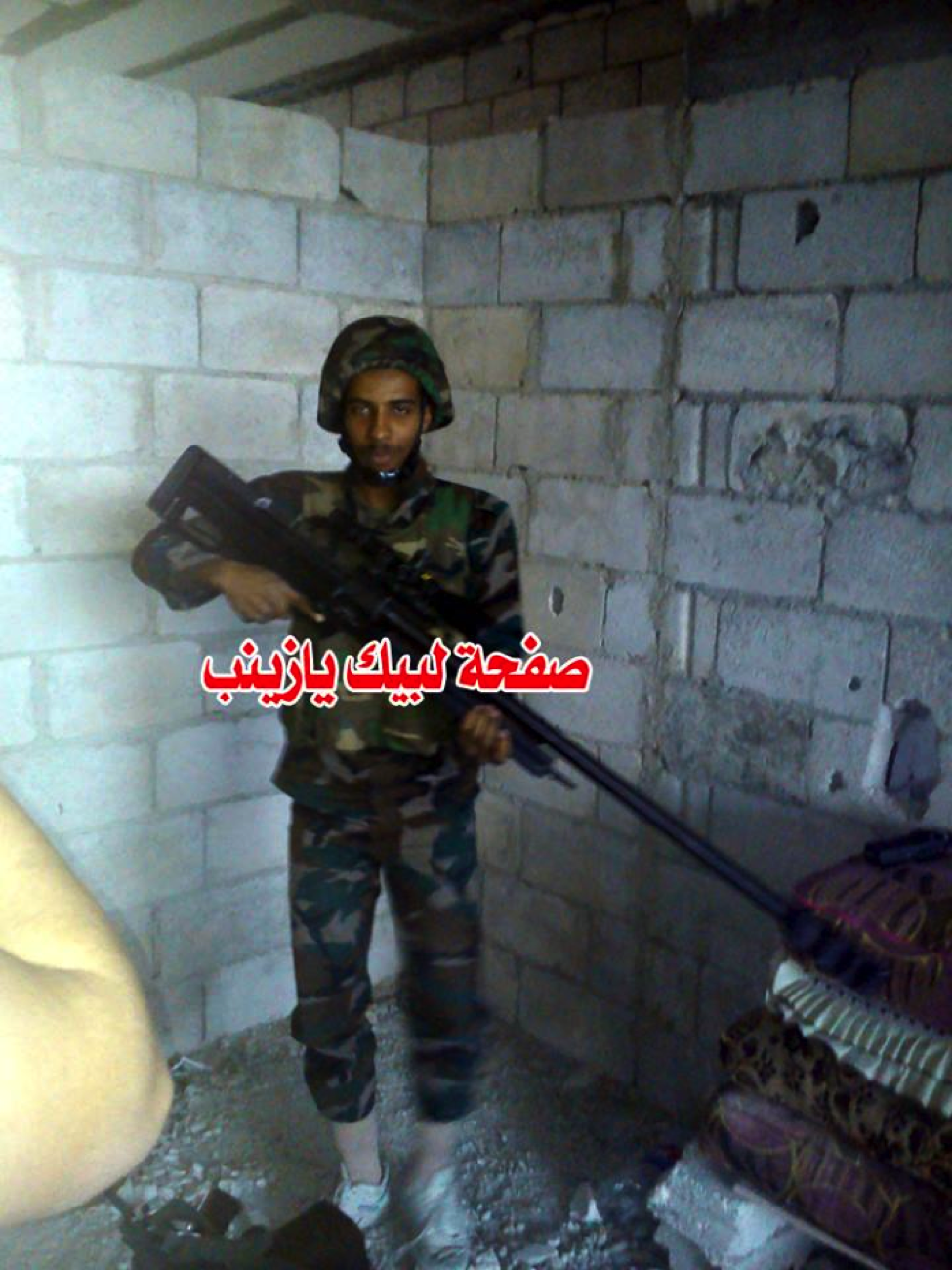

Figure 12: The Shia militia effort’s “first African martyr” (Muhammed Suleiman al-Kuwni) is shown holding the rifle.
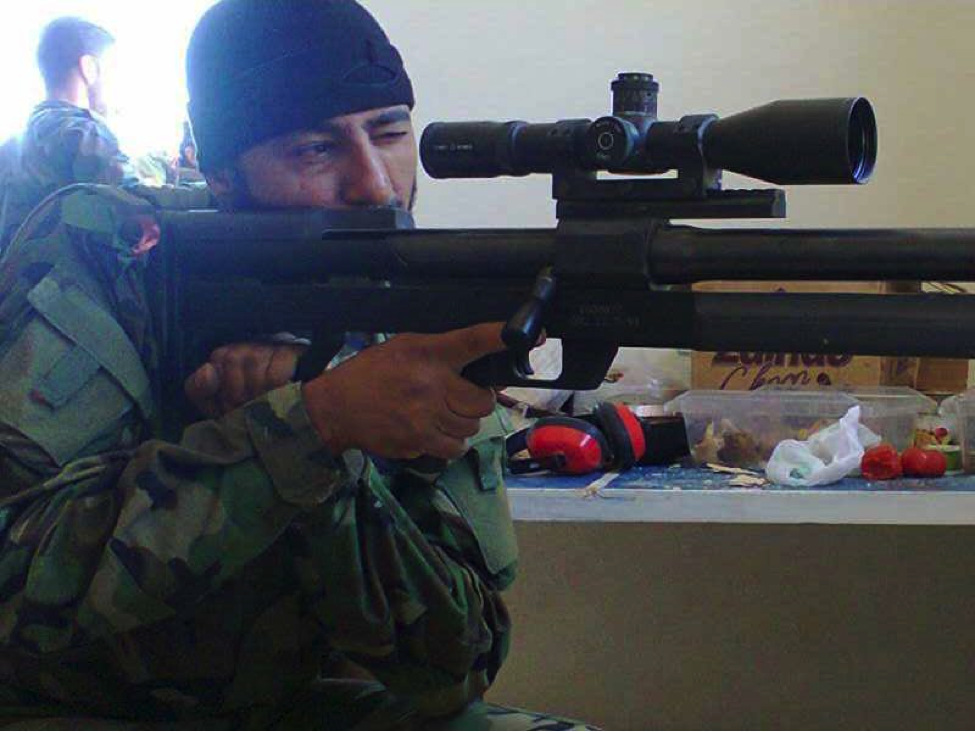

Figure 13: A fighter from an unnamed Shia Islamist militia (likely Liwa’a ‘Ammar Ibn Yasir) take aim with his rifle.
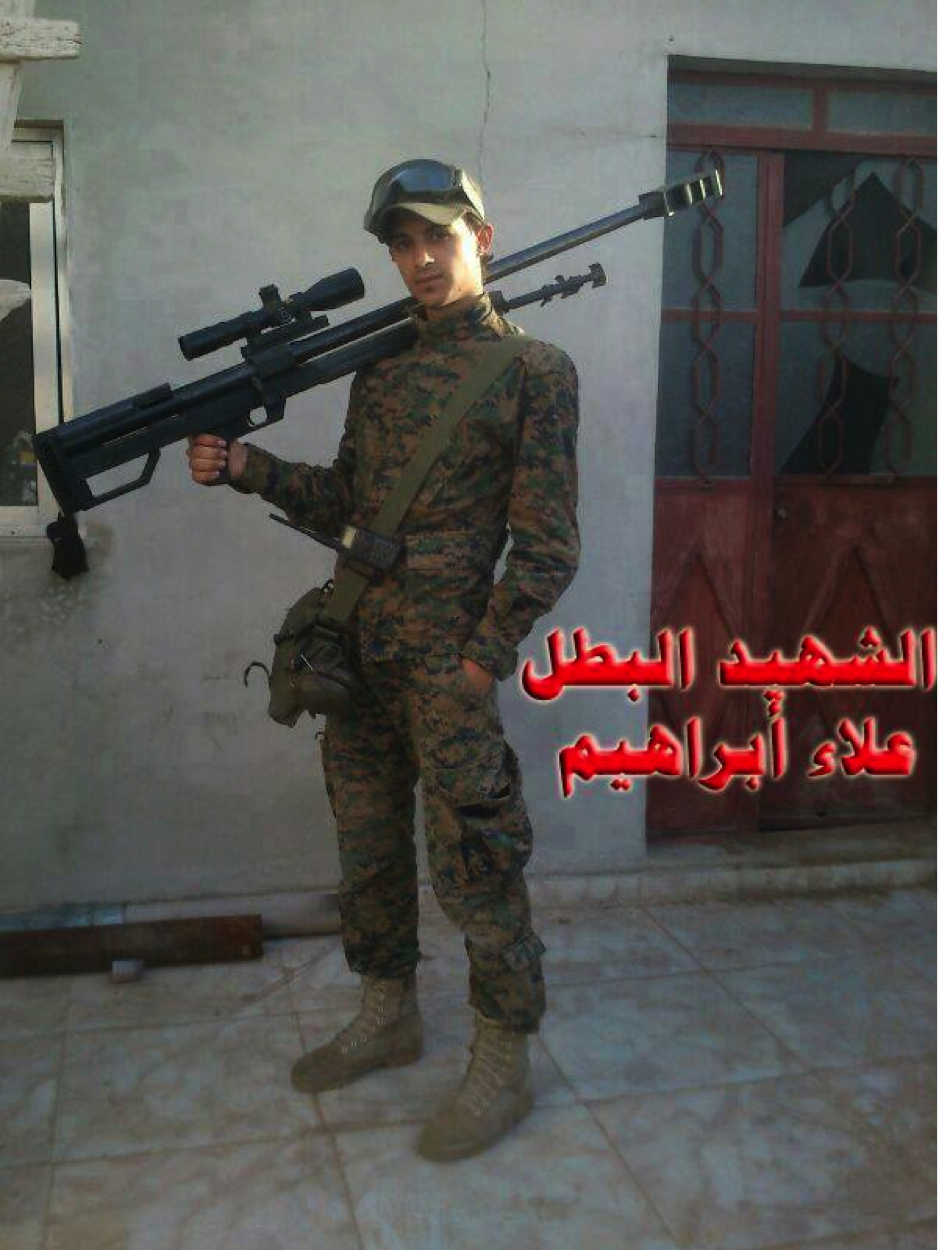

Figure 14: Alla’ Ibrahim (possibly from Liwa’a Zulfiqar), an Iraqi Shi’a fighter buried on November 30, 2013 holds the rifle over his shoulder.

Figure 15: An edited shot of Alla’ Ibrahim shows him posting with the rifle.
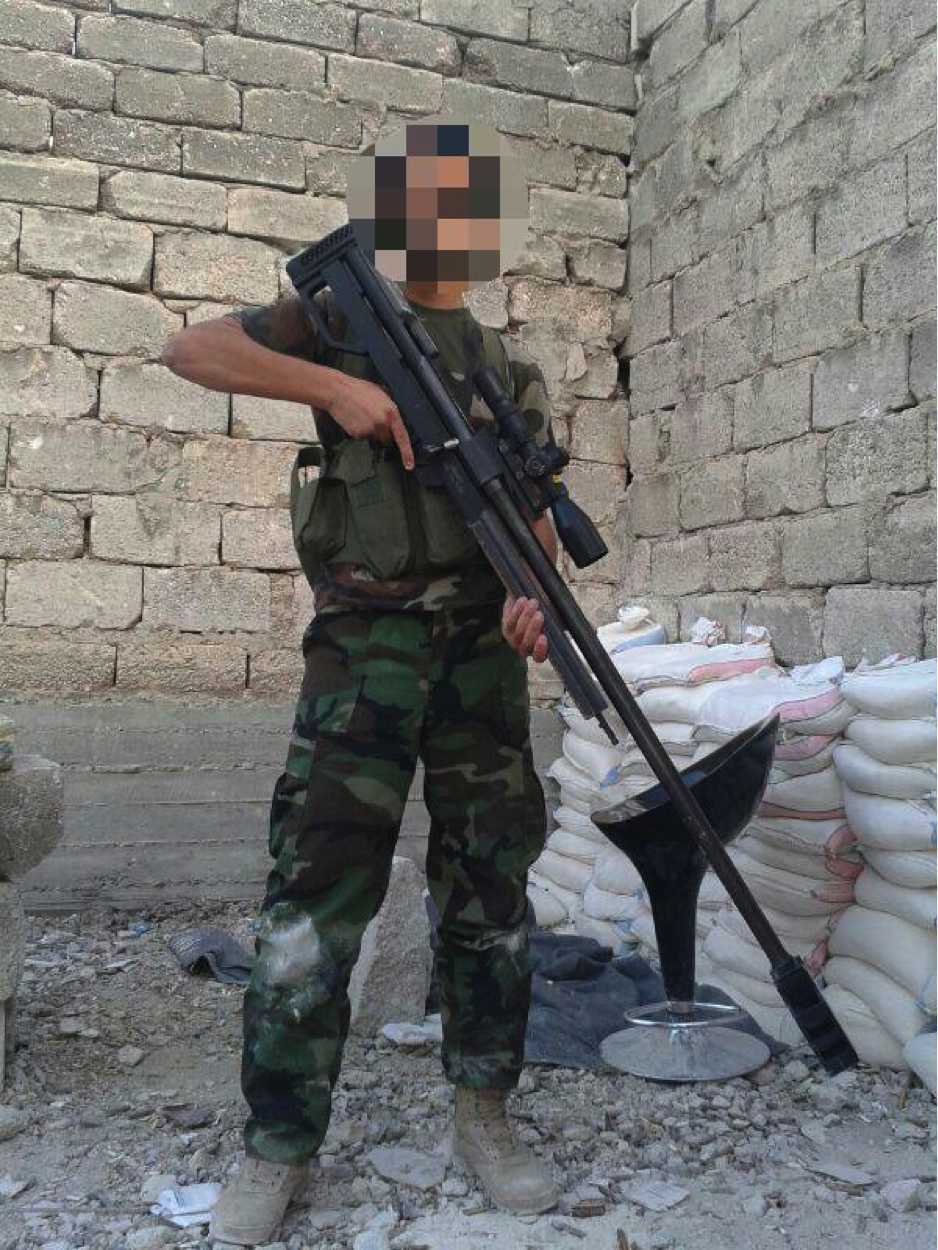

Figure 16: A Shia fighter from an unnamed militia group is shown with the HS. 50-type rifle.
[1] The Oryx Blog has an excellent post on HS. 50-type rifles in Syria: https://spioenkop.blogspot.com/2013/04/syria-and-her-hs50s.html. The post is from April 27, 2013 and pictures of Liwa’a Abu Fadl al-Abbas members with the rifle.
[2] See: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/1542559/Iraqi-insurgents-using-Austrian-rifles-from-Iran.html
[3] See: https://brown-moses.blogspot.com/2013/04/anti-material-rifles-in-syria.html. See also: https://www.thefirearmblog.com/blog/2012/07/16/mysterious-iranian-50-cals-part-3/. This post by The Firearms Blog should also be read when assessing the rifle in question.
[4] See: https://www.facebook.com/permalink.php?story_fbid=477563188953409&id=174927625878471.
[5] See: https://www.dailytelegraph.com.au/news/opinion/taliban-remain-in-fear-of-lethal-strikes-writes-chris-masters/story-e6frezz0-1226504862496